
The adoption of hydrostatic pressure (i.e. passive operation), indicating that these fouling control measures can be eliminated, substantially simplifying the mechanical and operational complexity of submerged hollow fiber UF systems. Sustained conditions could be achieved without backwashing, air sparging or chemical cleaning (i.e. The present study investigated the contribution of different auxiliary fouling control measures to the permeability that can be sustained, with the intent of minimizing the mechanical and operational complexity of submerged hollow fiber UF membrane systems while maximizing their throughput capacity. Recent studies have demonstrated that sustained operation without fouling control measures is possible, but little is known regarding the conditions under which extended operation can be sustained with minimal to no fouling control measures. Most of the complexity is associated with auxiliary fouling control measures, which include backwashing, air sparging and chemical cleaning. The molecules slow down because they have a more difficult time getting through the denser medium.The widespread adoption of submerged hollow fibre ultrafiltration (UF) for drinking water treatment is currently hindered by the complexity and cost of these membrane systems, especially in small/remote communities. Solvent density: As the density of the solvent increases, the rate of diffusion decreases.Temperature: Higher temperatures increase the energy and therefore the movement of the molecules, increasing the rate of diffusion.Mass of the molecules diffusing: More massive molecules move more slowly, because it is more difficult for them to move between the molecules of the substance they are moving through therefore, they diffuse more slowly.The closer the distribution of the material gets to equilibrium, the slower the rate of diffusion becomes. Extent of the concentration gradient: The greater the difference in concentration, the more rapid the diffusion.Several factors affect the rate of diffusion: Additionally, each substance will diffuse according to that gradient. (credit: modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal)Įach separate substance in a medium, such as the extracellular fluid, has its own concentration gradient, independent of the concentration gradients of other materials.

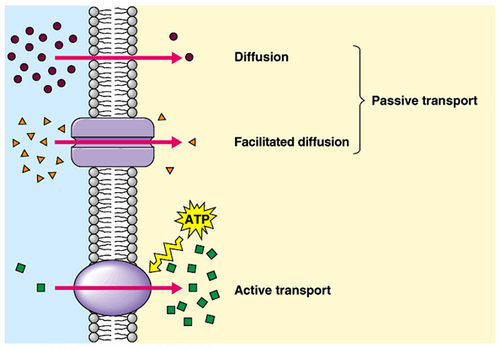
Figure 1 Diffusion through a permeable membrane follows the concentration gradient of a substance, moving the substance from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration.

Rather the different concentrations of materials in different areas are a form of potential energy, and diffusion is the dissipation of that potential energy as materials move down their concentration gradients, from high to low.

Materials move within the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion ( Figure 1). The perfume vapor will diffuse, or spread away, from the bottle, and gradually, more and more people will smell the perfume as it spreads. The perfume is at its highest concentration in the bottle and is at its lowest at the edges of the room. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of perfume in a room filled with people. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. Diffusionĭiffusion is a passive process of transport. A physical space in which there is a different concentration of a single substance is said to have a concentration gradient. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion. Passive transport is a naturally occurring phenomenon and does not require the cell to expend energy to accomplish the movement. The most direct forms of membrane transport are passive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
